|
Rhythmical-musical
experience, be it for aesthetic enjoyment or with an educational and
therapeutic purpose, assumes there are structures in humans which
follow musical conformities to a natural law. Music and musical movement are art forms which are realised in a time area and form time organisms. Of the basic elements of music (melodics, rhythmics, metrics, harmony, agogics, etc.), metrics, rhythmics and agogics are mainly temporal determinations. Melodics and harmony are at first glance more likely to present elements of an aesthetic content, but they also are ultimately based on regulating features determined by time with regard to tonal steps and tonal conditions. There is therefore sufficient reason to search for biological time structures in humans which can be considered for the musical work and experience as equivalent or reagent - whatever their nature might be. Particularly in view of the educational and therapeutic resources of music, it is likely to be of importance to know in which way and where musical-temporal function orders and structures are realised in the organism. The results of modern chronobiology and chronomedicine have shown that the human organism does not only have a complicated interior design in terms of space structure, but also has a highly sophisticated time design which is built up from numerous rhythmical time structures. |
|||
|
 |
||
|
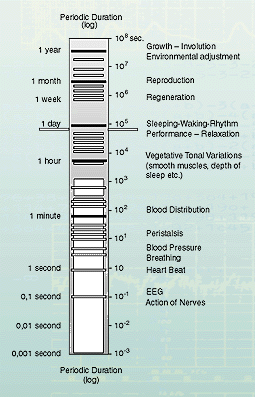
Illustration 1 Overview
of the favoured periodic duration (frequency ranges) of the rhythmic
functions in humans. The scale of periodic duration is divided logarithmically.
The stable frequency ranges of the spontaneous rhythms are specially
emphasised. |
|||
|
|
|||
| B A S I C M U S I C M E D I C I N E R E S E A R C H |
|
The
Biological Fundamentals of the Digital Stress Management Chronobiological Aspects of Music Physiology continued |