|
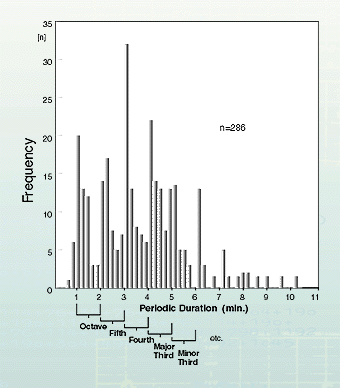
In contrast, the rhythms of the metabolic system can no longer be modulated in their frequency. On the contrary, each functional area has a series of different pre-formed frequency bands which, according to the demands on performance, are utilised in a rapidly changing manner. All these frequency bands, however, relate to each other in simple whole numbered frequencies, and are so subject to a harmonic-musical order. The rhythm of the stomach peristalsis, for instance, with its wave interval of approx. 20 seconds has a frequency ratio of 3:1 compared to the one-minute basic rhythm of the fundus musculature of the stomach and the contraction rhythm of the duodenum a ratio of 4:1 compared to the rhythm of the stomach peristalsis. An isolated piece of smooth intestinal musculature shows spontaneous-rhythmic contractions whose periodic duration constantly changes in whole numbered jumps (illustration 8). There are probably musical-harmonic time structures embodied in each individual cell which correspond to the harmonic interval proportions. |
|
 |
|
|
|
| <<
>>
With kind permission of AAR EDITION © AAR EDITION INTERNATIONAL 2001 |
| B A S I C M U S I C M E D I C I N E R E S E A R C H |
|
The
Biological Fundamentals of the Digital Stress Management Chronobiological Aspects of Music Physiology continued |