|
In this context, it should also be of interest that the frequency and phase co-ordination of the heart rhythms of mother and child in the womb also participate in this nocturnal intensification of the rhythmic functional orders. Thus, it could be proven that, while pregnant women were asleep at night, not only is the heart rate ratio of mother and child more strictly adjusted to the whole numbered value of 1:2, but that, at the same time, a phase co-ordination sets in during which the child's heart beat prefers certain phases of its mother's heart beat. (illustration 15). At the same time, this example makes the functional importance of harmonic co-ordination between rhythmic functions clear, as with correct phase co-ordination, an uneconomical-simultaneous arrival of the mother's and child's pulse waves in the placenta can be avoided. |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||
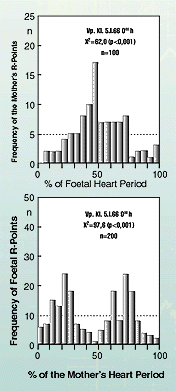 |
Illustration 15 Frequency distributions of 100 R-Point starting in the ECG of a pregnant woman over the foetal heart rate measured in the ECG by R-Point to R-Point and divided into 20 classes of 5% of the heart periodic duration. Below: Frequency distributions of the foetal R-Point, starting with the mother's heart period during the same test. The measurements were carried out during the nocturnal sleep of the pregnant women. The Chi-square-values refer to the deviation of the class frequencies of the average expected value (hatched horizontal). (According to HILDEBRANDT and KLEIN 1979) |
||||
|
|
|||||
| B A S I C M U S I C M E D I C I N E R E S E A R C H |
|
The
Biological Fundamentals of the Digital Stress Management Chronobiological Aspects of Music Physiology continued |